This balance sheet compares the financial position of the company as of September 2020 to the financial position of the company from the year prior. A few examples of footnotes in the balance sheet could include claims against the company, methods of depreciation, or the method of valuing inventory. Taxes Payable – Taxes that have accrued but have not yet been paid. The wages have been paid to the employee but payroll taxes haven’t been paid yet as they weren’t due at the specific time period. For more resources, check out our business templates library to download numerous free Excel modeling, PowerPoint presentations, and Word document templates. The return on equity ratio shows the ratio of income to shareholder’s equity.
Criticisms of Balance Sheet Formulas
This simply lists the amount due to shareholders or officers of the company. The balance sheet is a report that gives a basic snapshot of the company’s finances. This is an important document for potential investors and loan providers. This is the value of funds that shareholders have invested in the company.
Balance Sheets Examine Risk
Ensure that you meet your financial obligations and solvency goals with this easy-to-use monthly balance sheet template. Enter your assets — including cash, value of inventory, and short-term and long-term investments — as well as liabilities and owner’s equity. Completing the form will provide you with an accurate picture of your finances.
- Balance sheets allow the user to get an at-a-glance view of the assets and liabilities of the company.
- Explore our finance and accounting courses to find out how you can develop an intuitive knowledge of financial principles and statements to unlock critical insights into performance and potential.
- If you are a shareholder of a company or a potential investor, it is important to understand how the balance sheet is structured, how to read one, and the basics of how to analyze it.
Financial Ratios and the Balance Sheet
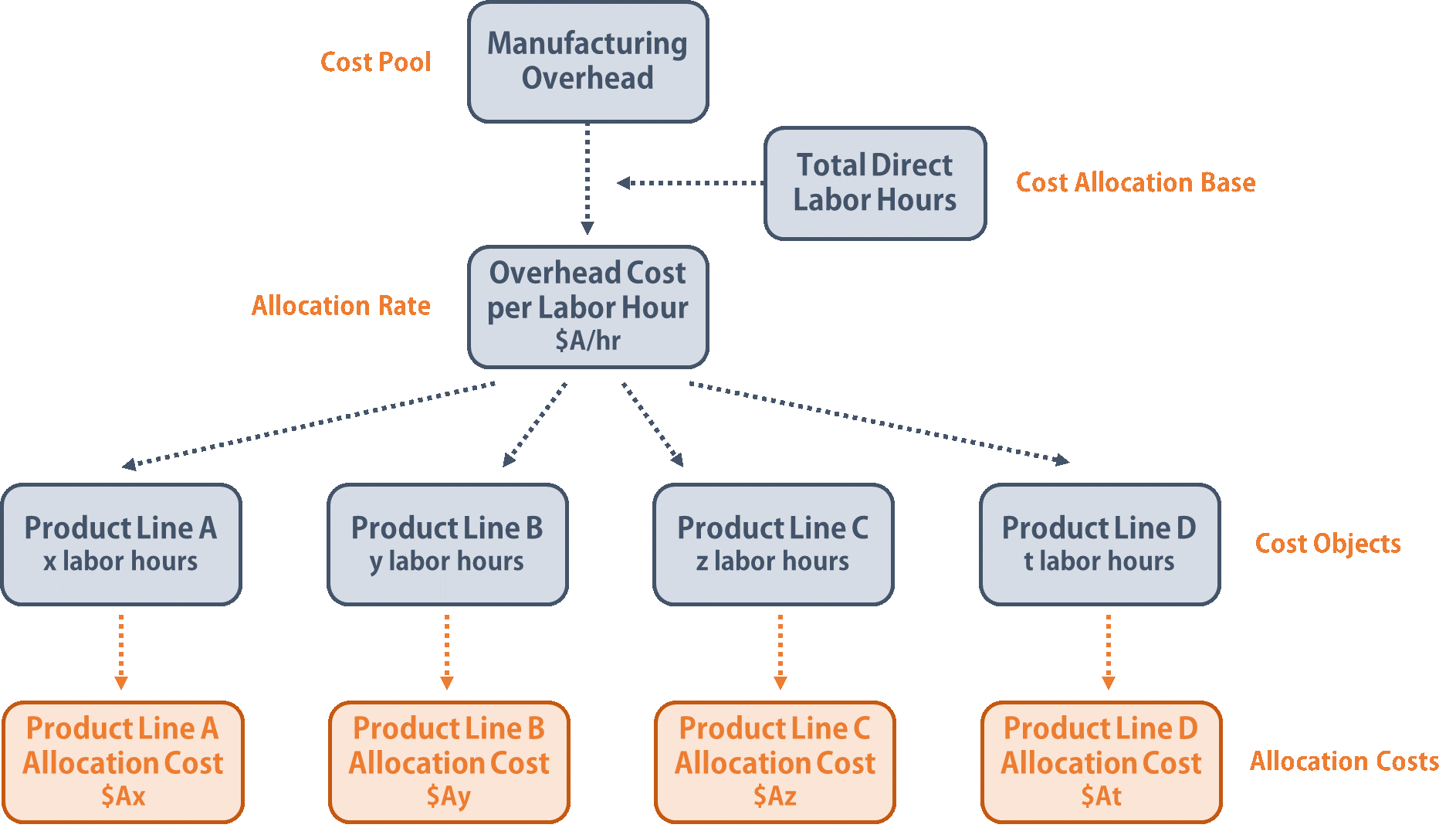
All liabilities that are not current liabilities are considered long term liabilities. Depicting your total assets, liabilities, and net worth, this document offers a quick look into your financial health and can help inform lenders, investors, or stakeholders about your business. Based on its results, it can also provide you key insights to make important financial decisions. A company’s balance sheet is one of the most important financial statements it produces—typically on a quarterly or even monthly basis (depending on the frequency of reporting). A balance sheet provides a summary of a business at a given point in time. It’s a snapshot of a company’s financial position, as broken down into assets, liabilities, and equity.
Noncurrent Liabilities
Enter your name and email in the form below and download the free template now! You can use the Excel file to enter the numbers for any company and gain a deeper understanding of how balance sheets work. Shareholder equity is not directly related to a company’s market capitalization.
A business can prepare the balance sheet in several ways, but accounting software is the easiest. A business owner, bookkeeper, or accountant usually prepares the balance sheet. Current assets refer to assets that a company can easily convert into cash within a financial year. This category includes readily available funds in the bank, inventory stock, and accounts receivable, which is money owed to the company by its customers. These assets are crucial for ensuring a company’s liquidity and its ability to meet short-term obligations.
Definition and Examples of Balance Sheet Formulas
Total liability is typically ordered with total current liabilities first and then non-current liabilities. Accounts Payable – Similar to accounts receivable, accounts payable are short-term loans, typically owed by the business from purchases made on credit from suppliers or vendors. The reason for dividing current and long-term assets is that these categories can be used to measure the liquidity of a company by turning assets into cash. The balance sheet is prepared by either a business owner, bookkeeper or accountant. If Companies House requires it, an accountant is the best person to prepare and submit the accounts, as they will know the generally accepted accounting principles. The easiest way to prepare a balance sheet is to use an accounting software package, which will automatically produce the report from the reports list.
A balance sheet is also always in balance, where the value of the assets equals the combined value of the liabilities and shareholders’ equity. It should not be surprising that the diversity of activities included among publicly-traded companies is reflected in balance sheet account presentations. In these instances, the investor will have to make allowances and/or defer to the experts. Shareholders’ equity refers generally to the net worth of a company, and reflects the amount of money that would be left over if all assets were sold and liabilities paid. Shareholders’ equity belongs to the shareholders, whether they’re private or public owners. It’s important to note that how a balance sheet is formatted differs depending on where an organization is based.
Noncurrent or long-term liabilities are debts and other non-debt financial obligations that a company does not expect to repay within one year from the date of the balance sheet. Measuring a company’s net worth, a balance sheet shows what a company owns and how these assets are financed, either through debt or equity. Overall, a balance sheet is an important statement of your company’s financial health, and it’s important to have accurate balance sheets available regularly.
When paired with cash flow statements and income statements, balance sheets can help provide a complete picture of your organization’s finances for a specific period. By determining the financial status of your organization, essential partners have an informative blueprint of your company’s potential and profitability. This balance sheet template provides you with a foundation to build your own company’s financial statement showing the total assets, liabilities, and shareholders’ equity. A company’s balance sheet is one of three financial statements used to give a detailed picture of the health of a business.
For example, imagine a company reports $1,000,000 of cash on hand at the end of the month. Without context, a comparative point, knowledge of its previous cash balance, and an understanding of industry operating demands, knowing how much cash on hand a company has yields limited value. Investors and analysts alike use balance sheet formulas to gain insight about a company’s finances. Track your quarterly financial https://www.business-accounting.net/ position by entering each month’s assets and liabilities and reviewing the monthly and quarterly perspectives of your owner’s equity. Monthly columns provide you with assets, liabilities, and equity tallies, and also reflect three-month figures for each quarter. This is the perfect template for short-term analysis of fiscal health but can be used for year-over-year monthly and quarterly comparisons.
Download the sample template for additional guidance, or fill out the blank version to provide a financial statement to investors or executives. The balance sheet includes information about a company’s assets and liabilities, and the shareholders’ equity that results. These things might include short-term assets, such as cash and accounts receivable, inventories, or long-term assets such as property, plant, and equipment (PP&E). Likewise, its liabilities may include short-term obligations such as accounts payable to vendors, or long-term liabilities such as bank loans or corporate bonds issued by the company. A company’s balance sheet, also known as a “statement of financial position,” reveals the firm’s assets, liabilities, and owners’ equity (net worth) at a specific point in time.
It shows in one place how much the business owns (assets) and owes (liabilities). The report is used by business owners, investors, creditors and shareholders. Fixed assets or long-term assets are things a business owns that it plans to use for a long period of time. To complete your balance sheet template you’ll need to add in details about the debts and liabilities your company owes. Different industries, and therefore different companies, may have slight variations in reporting standards. Looking under the surface of these figures lets analysts and investors see how the business is doing financially, and compare one company to another.
A balance sheet template is a tool for tallying your assets and liabilities so that you can calculate your equity. Use a balance sheet template to ensure you have sufficient funds to meet and exceed your financial obligations. These provide additional information pertaining to a company’s operations and financial position and are considered to be an integral part of the financial statements. Liabilities are obligations to parties other than owners of the business. They are grouped as current liabilities and long-term liabilities in the balance sheet. Current liabilities are the obligations that are expected to be met within a period of one year by using current assets of the business or by the provision of goods or services.
The left side of the balance sheet outlines all of a company’s assets. On the right side, the balance sheet outlines the company’s liabilities and private vs public accounting shareholders’ equity. The balance sheet is one of the three primary financial statements that a business uses to evaluate its financial health.